Liquid Fuel from Microbial Communities
Technology Description:
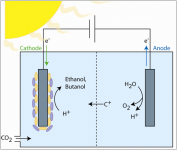
Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) is developing an engineered system to create liquid fuels from communities of interdependent microorganisms. MUSC is first pumping carbon dioxide (CO2) and renewable sources of electricity into a battery-like cell. A community of microorganisms uses the electricity to convert the CO2 into hydrogen. That hydrogen is then consumed by another community of microorganisms living in the same system. These new microorganisms convert the hydrogen into acetate, which in turn feed yet another community of microorganisms. This last community of microorganisms uses the acetate to produce a liquid biofuel called butanol. Similar interdependent microbial communities can be found in some natural environments, but they've never been coupled together in an engineered cell to produce liquid fuels. MUSC is working to triple the amount of butanol that can be produced in its system and to reduce the overall cost of the process.
Potential Impact:
If successful, MUSC would create a liquid transportation fuel that is cost competitive with traditional gasoline-based fuels and 10 times more efficient than existing biofuels.
Security:
Cost-competitive electrofuels would help reduce U.S. dependence on imported oil and increase the nation's energy security.
Environment:
Widespread use of electrofuels would help limit greenhouse gas emissions and reduce demands for land, water, and fertilizer traditionally required to produce biofuels.
Economy:
A domestic electrofuels industry could contribute tens of billions of dollars to the nation's economy. Widespread use of electrofuels could also help stabilize gasoline prices—saving drivers money at the pump.
Contact
ARPA-E Program Director:
Dr. Eric Rohlfing
Project Contact:
Dr. Harold May
Press and General Inquiries Email:
ARPA-E-Comms@hq.doe.gov
Project Contact Email:
mayh@musc.edu
Partners
CDM Smith
University of South Carolina
Clemson University
Related Projects
Release Date:
02/07/2009
