ARPA-E Investor Update Vol. 12: Syzygy Plasmonics' All-Electric Photoreactor
ARPA-E awardee Syzygy Plasmonics recently raised $76 million in Series C funding from Carbon Direct Capital along with Aramco Ventures, Chevron Technology Ventures, Lotte Chemical, and Toyota Ventures. Early investors in Syzygy also joined the round, including EVOK Innovations, The Engine, Equinor Ventures, Goose Capital, Horizons Ventures, Pan American Energy, and Sumitomo Corporation of Americas. Syzygy previously raised over $35 million in public and private funding for their novel technology.
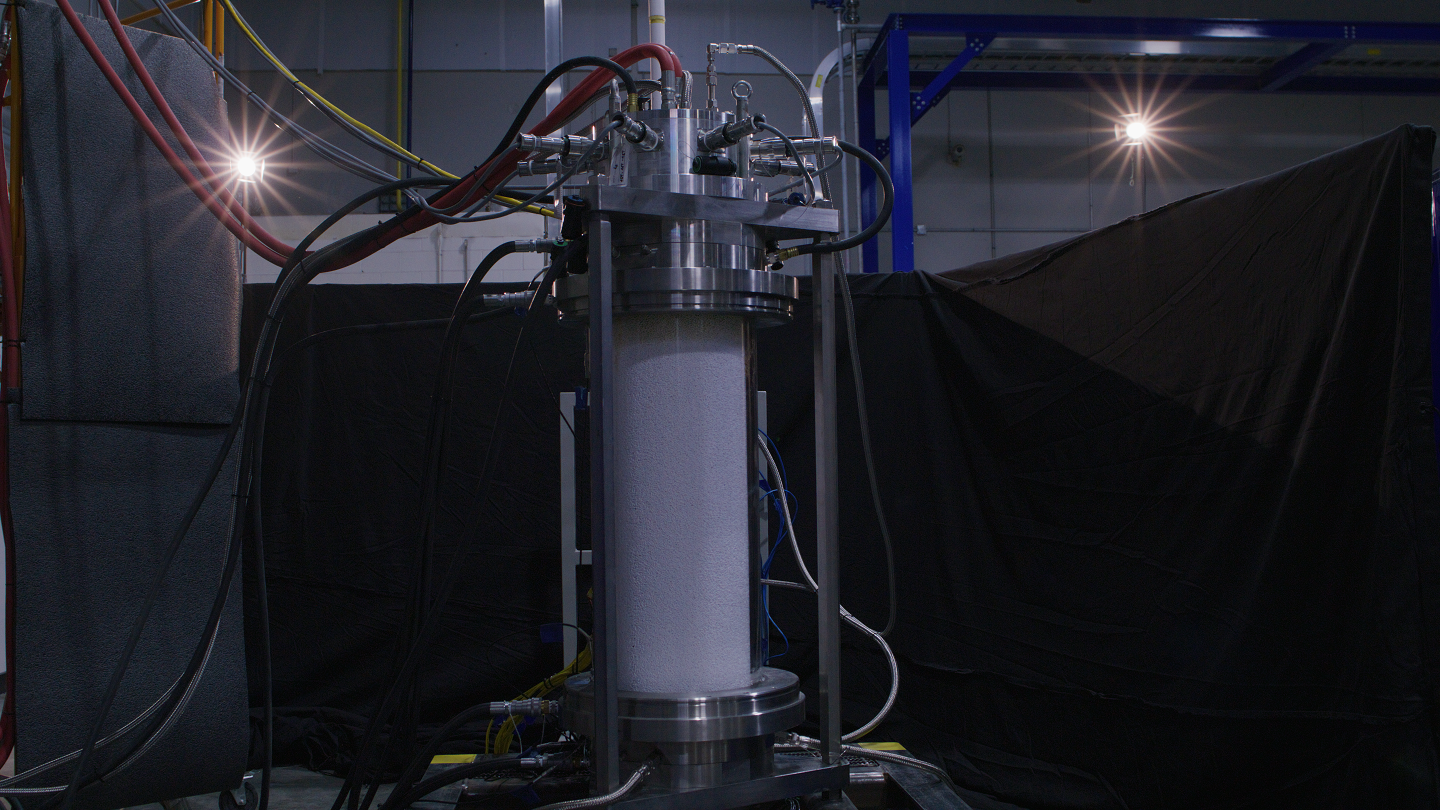
Syzygy’s breakthrough technology provides a deep decarbonization platform that relies on light, rather than heat, removing the need for combustion and increasing efficiency while reducing emissions. They have developed a universal, commercially scalable photoreactor from cheap, easily sourced materials to house their unique photocatalytic reaction, allowing for greater energy efficiency.
Syzygy previously received $750,000 as part of ARPA-E’s OPEN 2018 program. The purpose of the OPEN program is to identify high-potential projects outside of ARPA-E’s current portfolio. Syzygy’s technology met the need for a commercially feasible, scalable photocatalytic reactor that produces low-cost and on-demand hydrogen gas at the point-of-use. ARPA-E funding went towards the development of their P-DATM photoreactor.
With this $76 million in funding, Syzygy plans to continue development of their all-electric reactor systems. The company plans to launch their P-DATM photoreactor in 2023. The P-DATM has the potential to create green hydrogen from green ammonia and renewable electricity. Green hydrogen is a term for hydrogen produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity. Green ammonia is ammonia produced in a renewable and carbon-free production process. The goal is to eliminate all fossil fuel-based combustion from the chemical manufacturing process and to reduce the carbon emissions of hydrogen.
To stay on track for net zero emissions by 2050, hydrogen production must double by 2030, with most of that production resulting in low carbon emissions. Ammonia is a useful form of transporting hydrogen, due to lowered costs and the ability to transport greater quantities for longer distances. Using ammonia to store and transport green hydrogen requires technologies to make green ammonia and convert it back to hydrogen. Syzygy's technology provides the tools to convert green ammonia into green hydrogen.
Syzygy’s technology has the potential to transform the chemical manufacturing industry by shifting it to renewable electricity and thereby reducing its carbon footprint.
