Advanced Heat Exchangers
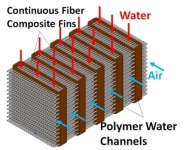
Technology Description:
The University of Wisconsin (UW-Madison) and its partner Oak Ridge National Laboratory will develop enabling technologies for low-cost, high-performance air-cooled heat exchangers. The objective is to create an optimization algorithm in order to identify and design a novel heat exchanger topology with very high heat transfer performance. The team also plans to develop a high-thermal conductivity polymer composite filament that can be used in additive manufacturing (3D printing) to produce the high-performance heat exchanger design. Due to the design freedom enabled by additive manufacturing, the team plans to develop 3D heat exchanger geometries that optimize heat transfer and decrease the total footprint required for an air-cooled system. Both of these innovations could enhance air-side heat transfer and improve the efficiency and cost of heat exchangers.
Potential Impact:
If successful, UW-Madison’s innovative heat exchanger design will lower the cost of air-cooling systems without reducing the efficiency of power plant cooling.
Security:
Enhanced air-cooled heat exchangers could help power plants maintain energy efficiency when the use of water for cooling is restricted.
Environment:
The team’s affordable, compact design reduces the need for water in power plant cooling and could also be used to decrease water use in other applications, such as HVAC systems.
Economy:
The project team estimates that, by utilizing additive manufacturing and improving the efficiency of heat exchangers, the system could be an economical way to cool power plant condenser water.
Contact
ARPA-E Program Director:
Dr. David Tew
Project Contact:
Gregory Nellis
Press and General Inquiries Email:
ARPA-E-Comms@hq.doe.gov
Project Contact Email:
gfnellis@engr.wisc.edu
Partners
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Related Projects
Release Date:
09/26/2014
