Plasma Liners For Fusion
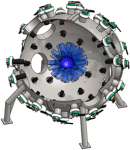
Technology Description:
Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), along with HyperV Technologies and other partners, will design and build a new driver technology that is non-destructive, allowing for more rapid experimentation and progress toward economical fusion power. The team will use a spherical array of plasma guns to produce supersonic jets that merge to create an imploding plasma liner. Because the guns are located several meters away from the fusion burn region (i.e., they constitute a “standoff driver”), the reactor components should not be damaged by repeated experiments. This will allow the team to perform more rapid experimentation, allowing them to better understand the behavior of plasma liners as they implode. If successful, the project will demonstrate the validity of this driver design, optimize the precision and performance of the plasma guns, and obtain experimental data on ram-pressure scaling and liner uniformity critical to progress toward an economical fusion reactor.
Potential Impact:
If successful, LANL’s work will validate a new driver approach, which will enable a low-cost, rapid development path towards economical fusion power.
Security:
LANL’s innovation could accelerate the development of cost-effective fusion reactors, which may provide a nearly limitless supply of domestic power and eliminate dependence on foreign sources of energy.
Environment:
Fusion reactors offer nearly zero emissions and produce manageable waste products. If widely adopted, they could significantly reduce or nearly eliminate carbon emissions from the electricity generation sector.
Economy:
LANL’s approach, if viable, could enable a low-cost path to fusion, reducing research costs to develop economical reactors.
Contact
ARPA-E Program Director:
Dr. Robert Ledoux
Project Contact:
Samuel Langendorf
Press and General Inquiries Email:
ARPA-E-Comms@hq.doe.gov
Project Contact Email:
samuel.langendorf@lanl.gov
Partners
Tech-X Corporation
University of New Mexico
HyperV Technologies Corp.
Brookhaven National Laboratory
University of Alabama, Huntsville
Related Projects
Release Date:
08/24/2014
