Robotic Personal Conditioning Device
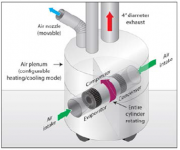
Technology Description:
The University of Maryland (UMD) will develop a robotic personal attendant providing improved comfort levels for individuals in inadequately heated/cooled environments. This mobile robotic platform will be fitted with a small, battery-powered, high-efficiency vapor compression heat pump and will be highly portable and able to follow an assigned person around during the course of the day, providing localized heating and/or cooling as needed while reducing the energy required to heat and cool buildings.
Potential Impact:
If successful, DELTA technology could increase energy efficiency, reduce emissions produced by powering traditional HVAC systems, and enable more sustainable heating and cooling architectures for energy-efficient building design.
Security:
The innovations developed under the DELTA program have the potential to increase energy efficiency, improve overall building performance, and reduce HVAC energy consumption by at least 15%.
Environment:
The heating and cooling of buildings generates about 13% of the U.S. domestic greenhouse gas emissions. Through improved utilization of energy produced by fossil fuels with full adoption DELTA can reduce these emission by 2%.
Economy:
DELTA program innovations can help U.S. businesses eventually reduce reliance on tightly controlled building environments, thus enabling radical and sustainable architecture in next generation energy efficient building design
Contact
ARPA-E Program Director:
Dr. Jennifer Gerbi
Project Contact:
Dr. Reinhard Radermacher
Press and General Inquiries Email:
ARPA-E-Comms@hq.doe.gov
Project Contact Email:
raderm@umd.edu
Partners
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Sandia National Laboratory
Related Projects
Release Date:
04/29/2014
