
ARPA-E Investor Update Vol. 9: Ion Storage Systems' Solid-State Battery
Ion Storage Systems (ION) recently raised more than $30 million in its Series A funding round for their novel approach to solid-state batteries. The funding round included several investors, including Toyota Ventures. Their recently announced investment will enable ION to establish a battery cell manufacturing line for their next-generation solid-state batteries. Funds raised in the Series A round will also drive the company’s current development projects forward in the consumer electronics, automotive, and stationary storage markets.
ARPA-E first funded the team as a University of Maryland (UMD) project under the RANGE program, which focused on developing transformational electrochemical energy storage technologies to accelerate the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) by improving driving range and safety while lowering costs. The UMD team set out to develop ceramic materials and processing methods to enable high-power, solid-state lithium metal anode batteries (LiB) for use in EVs. Current technology suffers from performance limitations that incremental progress cannot address. Unlike the conventional Li-ion batteries used in EVs that require heavy protective components, the UMD technology uses no liquids, allows greater abuse tolerance, has higher energy, and offers reduced weight.
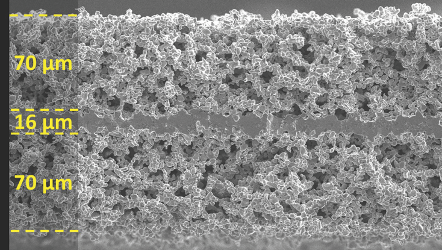
Sample unfilled garnet tri-layer porous electrolyte with dense interlayer
The UMD team built a tri-layer electrolyte structure from Li7La3Zr2O12 (“LLZO”), a new garnet-ceramic material with a room temperature conductivity nearly equivalent to state-of-the-art liquid electrolytes used in lithium ion batteries and in LiB. It features a porous structure for both the positive and negative electrodes, with a dense, thin, solid electrolyte sandwiched between them. The team also leveraged a new atomic layer deposition technique in which a thin aluminum oxide (or other composition) coating is deposited onto the garnet electrolyte surfaces. The team’s technology combines a highly conductive lithium electrolyte, a rigid, self-supporting architecture, and low internal resistance. Together, these elements enable safe, inexpensive, and higher density batteries. UMD spun off a company, Ion Storage Systems, which began fabricating sample cells and distributing to potential customers. The technology continues to progress towards a new battery platform with higher capability, lower cost, and greater safety.

ION’s novel structure for solid state lithium-ion batteries
