Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
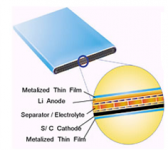
Technology Description:
Sion Power is developing a lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery, a potentially cost-effective alternative to the Li-Ion battery that could store 400% more energy per pound. All batteries have 3 key parts—a positive and negative electrode and an electrolyte—that exchange ions to store and release electricity. Using different materials for these components changes a battery's chemistry and its ability to power a vehicle. Traditional Li-S batteries experience adverse reactions between the electrolyte and lithium-based negative electrode that ultimately limit the battery to less than 50 charge cycles. Sion Power will sandwich the lithium- and sulfur-based electrode films around a separator that protects the negative electrode and increases the number of charges the battery can complete in its lifetime. The design could eventually allow for a battery with 400% greater storage capacity per pound than Li-Ion batteries and the ability to complete more than 500 recharge cycles.
Potential Impact:
If successful, Sion Power's project would encourage production of low-cost, high-energy, rechargeable Li-S batteries, contributing to the widespread adoption of EVs. Improving the number of recharge cycles limits battery replacements, saving drivers money.
Security:
Increased use of EVs would decrease U.S. dependence on foreign oil—the U.S. spends nearly $1billion per day on oil.
Environment:
Greater use of EVs would reduce greenhouse gas emissions, 28% of which come from the transportation sector.
Economy:
This battery would enable an EV to travel from Chicago to St. Louis (300 miles) on a single charge, for less than $10 on average.
Contact
ARPA-E Program Director:
Dr. Dane Boysen
Project Contact:
Dr. Yuriy Mikhaylik
Press and General Inquiries Email:
ARPA-E-Comms@hq.doe.gov
Project Contact Email:
ymikhaylik@sionpower.com
Partners
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
University of California, Berkeley
BASF
Related Projects
Release Date:
02/07/2009
